For many years, India has been known as The Land of Agriculture. With the dawn of the New Electronics Policy in 1984, and implementation of 1990’s Economic Reforms India started shaping it’s economy on the shoulder of Information Technology. Now after more than 25+ years of transformation, Information Technology and Software Services Vertical makes 25-30% of the Total Exports of India.
India has made a huge change to it’s export basket by creating an another pivot for it’s economy. A supporting document is attached herewith. Other Verticals where India has excelled are – Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals and the Mobile Manufacturing. To predict what is coming ahead for Indian Economy, you can scroll through following content
Table of Contents
Before we jump to the future transformation through Indian Export trends, Let’s Explore how India’s Export Portfolio performed as per 2022 statistics –
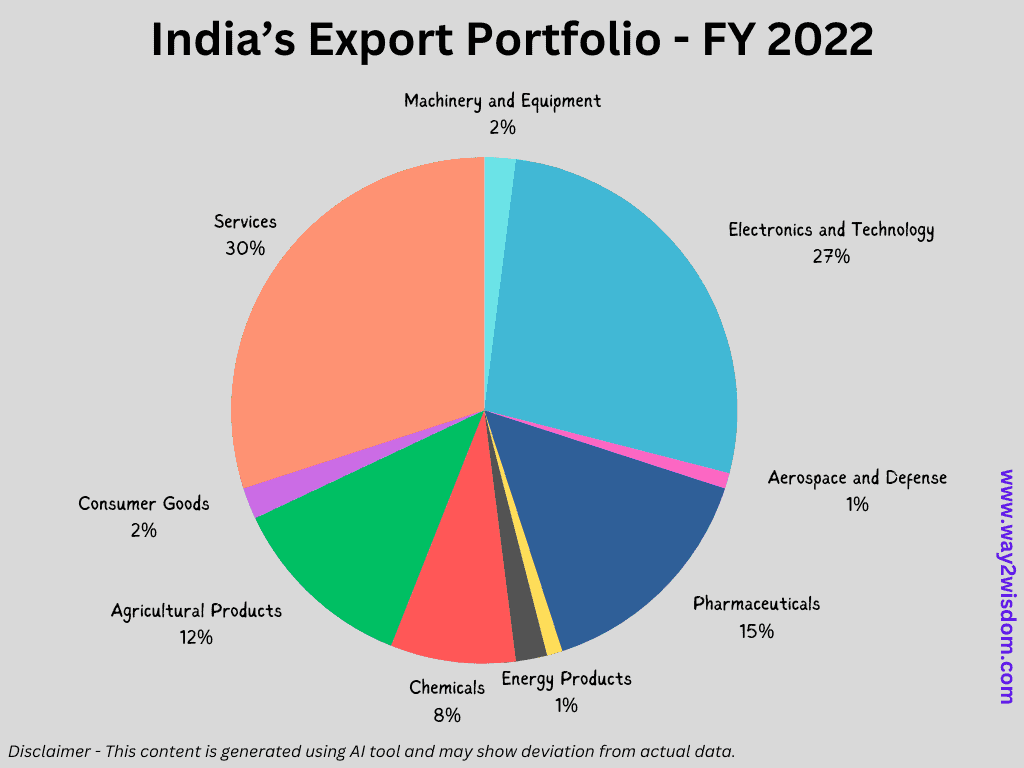
Now, let’s deep dive into the Exports Portfolio of India. Here we will list the verticals in the descending order of their contribution.
- Information Technology (IT) and Software Services: Approximately 25-30% of total exports.
- Pharmaceuticals: Around 10-15% of total exports.
- Textiles and Garments: Roughly 10-15% of total exports.
- Automobiles and Auto Components: About 5-10% of total exports.
- Gems and Jewelry: Approximately 10-15% of total exports.
- Chemicals and Petrochemicals: Around 10-15% of total exports.
- Engineering Goods: Approximately 5-10% of total exports.
- Agriculture and Food Products: Roughly 10-15% of total exports.
- Oil and Petroleum Products: About 10-15% of total exports.
- Iron and Steel: Approximately 5-10% of total exports.
- Marine Products: Roughly 5-10% of total exports.
- Leather and Leather Goods: Around 5-10% of total exports.
- Aerospace and Defense: Approximately 5-10% of total exports.
- Handicrafts and Handloom Products: Roughly 5-10% of total exports.
- Electronic Goods: Approximately 5-10% of total exports.
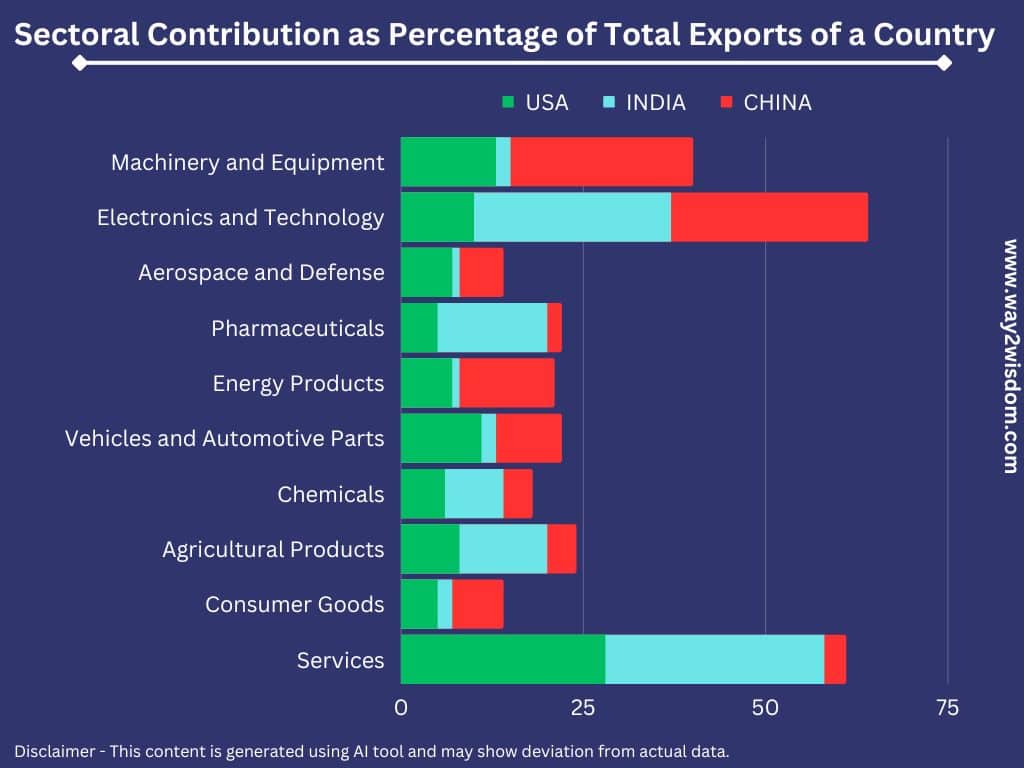
How Indian exports differ from developed economy?
Indian exports differ from those of developed economies in several key ways, reflecting the economic structure and stage of development of the country. Here are some of the primary differences:
- Export Composition: Indian exports are typically characterized by a mix of traditional and labor-intensive industries, such as textiles, agriculture, and handicrafts, alongside high-tech sectors like information technology (IT) and pharmaceuticals. In contrast, developed economies tend to have a more diverse range of exports, including advanced machinery, aerospace, and high-end manufacturing products.
- Value-Added Exports: Developed economies often engage in exports that involve higher value-added products and services. They may export advanced machinery, automobiles, electronics, and other technologically sophisticated goods. In contrast, India’s exports include a significant proportion of lower value-added goods and labor-intensive products.
- Technology and Innovation: Developed economies are at the forefront of technological innovation, and their exports frequently incorporate cutting-edge technology and research. Indian exports, while advancing in sectors like IT and pharmaceuticals, may not always exhibit the same level of technological sophistication.
- Scale and Volume: Developed economies typically have a larger volume of exports due to their larger markets and industrial capacity. India’s export volume, while significant, may be comparatively smaller.
- Market Access and Quality Standards: Exports from developed economies often face stringent quality and safety standards, and they are more likely to have easier access to international markets. Indian exporters may need to navigate a variety of trade barriers and meet stringent quality and safety requirements to access certain markets.
- Global Supply Chains: Developed economies are often key players in global supply chains, with components and intermediate goods crossing borders multiple times. Indian exporters, while increasingly integrated into global supply chains, may not be as deeply entrenched in some high-tech and advanced manufacturing supply chains.
- Services Exports: Developed economies often export a significant amount of services, including financial services, legal services, and consulting, in addition to goods. India, on the other hand, has gained prominence in the export of IT services, business process outsourcing, and software-related services.
- Trade Partners: Developed economies often have a broader range of trading partners, including both developed and emerging markets. India’s export destinations may be more concentrated in certain regions, with a significant portion going to specific countries or regions, such as the United States, the European Union, and neighboring countries.
- Agricultural Exports: India’s agricultural exports, including spices, tea, rice, and textiles, play a substantial role in its overall export profile. Developed economies usually have a smaller share of agricultural exports in their overall trade.
- Government Policies: The role of government policies, trade agreements, and subsidies in shaping India’s export profile may differ from those in developed economies.
It’s important to note that India’s export profile is evolving, and the country is making strides in high-value manufacturing, technology, and services. As the Indian economy continues to develop, its export composition is likely to change, and it may align more closely with the patterns observed in developed economies.

What are possible changes to export trends as India makes the transition from a developing nation to a developed one?
As India makes the transition from a developing nation to a developed one, its export trends are likely to undergo several changes. While these changes will depend on various factors, including government policies, global economic conditions, and industry developments, here are some possible changes in Indian export trends during this transition:
- Diversification and Complexity: India is likely to diversify its export portfolio and move towards more complex and technologically advanced products. This may include a greater focus on high-tech manufacturing, precision engineering, and advanced machinery.
- Services Dominance: The services sector, particularly IT and software services, is expected to continue to play a significant role in India’s exports. As India develops further, it may expand its services exports into areas like financial services, legal services, consulting, and education.
- Reduced Dependence on Labor-Intensive Industries: India may reduce its dependence on labor-intensive industries like textiles and low-value manufacturing as wages and production costs rise. The country will likely seek to move up the value chain in manufacturing and focus on automation and productivity improvements.
- Innovation and Research-Intensive Exports: As India invests more in research and development, it may increase exports of innovative and research-intensive products. This could include pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, aerospace, and advanced materials.
- Global Supply Chain Integration: India is expected to play a more substantial role in global supply chains, both in terms of manufacturing and services. This would involve greater integration with international value chains and cross-border collaboration.
- Quality and Standards Compliance: Meeting international quality and safety standards will become increasingly important for Indian exporters. The country will invest in quality control and compliance to access more markets.
- Market Diversification: India may diversify its export destinations, reducing its reliance on specific regions or countries. This can mitigate risk and provide access to a broader range of markets.
- Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Exports: There is a growing global demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products. India is likely to adapt by increasing its exports of green technologies, renewable energy solutions, and environmentally responsible goods.
- Trade Agreements and Economic Partnerships: As a developed nation, India may enter into more trade agreements and economic partnerships to facilitate exports. These agreements can open up new markets and ease trade barriers.
- Government Policies: Government policies will continue to shape India’s export trends. Policies promoting innovation, infrastructure development, ease of doing business, and foreign investment will have a significant impact on the country’s export capabilities.
- Enhanced Logistics and Infrastructure: Improved logistics and infrastructure will lead to more efficient transportation and distribution of goods, making Indian exports more competitive and reliable.
- Education and Skilled Workforce: Investments in education and skills development will ensure a qualified workforce capable of producing and exporting high-value goods and services.
- Currency Strength: A transition to a developed nation might see the Indian currency appreciate, which can impact the competitiveness of exports. The government will need to manage this aspect to maintain competitiveness in global markets.
It’s important to note that the transition from a developing to a developed nation is a complex and gradual process. These changes in export trends will take place over an extended period and will require a combination of strategic planning, investments, and policy adjustments to ensure a smooth transition and continued growth in India’s export sector.
At the End it is important to understand that – Predicting these shifts in the years to come will help you spot the Business and Investment Opportunities. As India breaks down the doors of the development, I will bring further updates to this post. Till then, Stay connected and follow the blog for more insightful content.
Disclaimer – Views are Personal. This article is for Educational Purposes only. This content is generated using AI tool and may show deviation from actual data.